1. Introduction
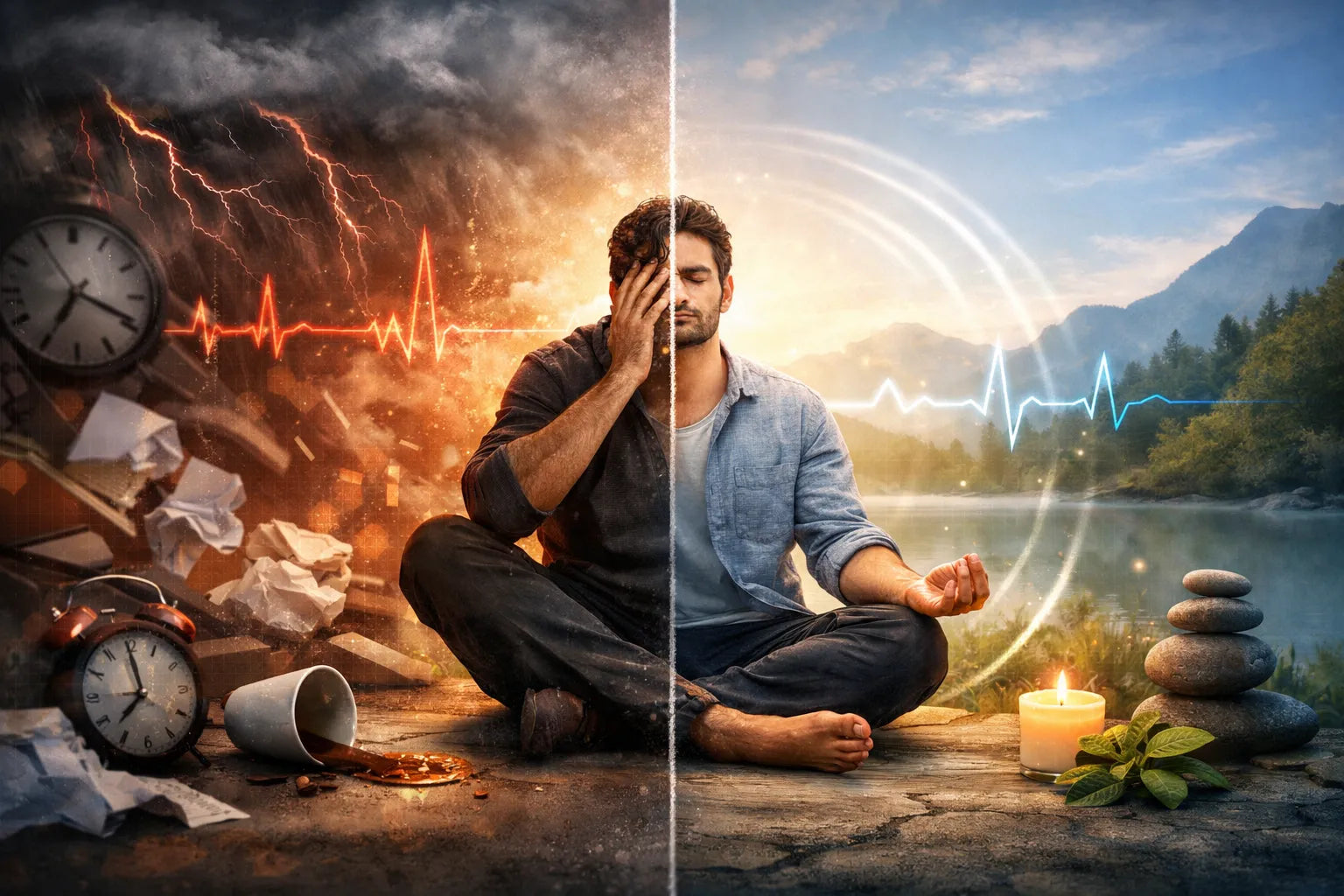
Human performance—whether physical, cognitive, or emotional—is fundamentally constrained by autonomic state regulation. High performance occurs when the nervous system is balanced: alert but not anxious, focused but not tense, energized but not overstimulated. Under chronic stress, fatigue, or operational demands, people often operate in maladaptive states of sympathetic overdrive, reducing clarity, reaction time, emotional stability, and decision-making capacity.
Shiftwave is a general wellness technology that integrates patterned mechanical vibration, breath-paced tactile cues, immersive sensory modulation, and zero-gravity posture to support the physiological conditions associated with optimal performance. It does not diagnose or treat any medical condition. Instead, it helps users access states of calm focus, restored readiness, and enhanced cognitive clarity.
This paper summarizes the scientific basis for these effects and presents observational and study-based findings that highlight Shiftwave’s potential as a performance-support tool.
2. Scientific Basis for Performance Enhancement
Optimal performance requires coordination of stress physiology, sensory processing, motor control, and attentional stability. Shiftwave’s modalities map to evidence-backed pathways influencing these domains.
2.1 Autonomic Regulation & Cognitive Performance
A large body of research shows that cognitive performance improves when the autonomic nervous system is balanced rather than hyperactivated.
-
Increased HRV is associated with improved executive function, attention, and emotional regulation (Laborde et al., 2017).
-
Vagal activation enhances cognitive flexibility and working memory (Hansen et al., 2003).
-
Reducing sympathetic dominance enhances decision-making accuracy (Suvada et al., 2020).
Shiftwave facilitates autonomic balance through:
-
Slow, resonant-frequency breath pacing
-
Vibration patterns synchronized with respiratory cycles
-
Somatosensory grounding
These mechanisms help users shift into a state of calm alertness, ideal for cognitive performance.
2.2 Mechanical Vibration & Physical Readiness
Mechanical vibration has documented effects on proprioception, neuromuscular activation, and perceived readiness:
-
Vibration enhances proprioceptive acuity, improving movement efficiency (Ritzmann et al., 2014).
-
Low-frequency vibration reduces muscle tension and improves circulation (Kerschan-Schindl et al., 2001).
-
WBV improves neuromuscular activation and reaction speed in athletes (Cardinale & Bosco, 2003).
Shiftwave’s patterned, full-body mechanical stimulation differs from exercise-based WBV but leverages the same mechanoreceptor pathways to:
-
decrease tension
-
increase body awareness
-
prime the neuromuscular system
-
produce a sense of physical readiness
2.3 Breathwork & Performance States
Breath control is a fundamental tool for performance across sports, tactical operations, and high-demand cognitive roles.
Research shows that slow breathing:
-
improves focus and sustained attention (Zaccaro et al., 2018)
-
stabilizes emotional responses during high-pressure tasks (Ma et al., 2017)
-
primes the body for calm concentration (“flow”) (Jerath et al., 2006)
Shiftwave automates breath entrainment using tactile wave patterns, making breathwork effortless and reliable, particularly for users who normally struggle with mindfulness-based performance tools.
2.4 Sensory Immersion & Attentional Stability
Attention is highly sensitive to sensory load. Multimodal immersion reduces noise and stabilizes focus:
-
Immersive environments improve attentional control and accuracy (Lindquist et al., 2012).
-
Sound-and-body synchronization increases alpha oscillations (associated with calm focus) (Ishimatsu et al., 2021).
-
Reducing competing sensory input enhances cognitive throughput (Brewer et al., 2011).
Shiftwave’s synchronized audio + tactile cues create a structured sensory field that supports deep focus and task readiness.
3. Performance Mechanisms in Shiftwave
Shiftwave supports performance using four evidence-backed pathways:
-
Calm Alertness
Autonomic regulation produces a high-performance blend of clarity + calm. -
Neuromuscular Readiness
Mechanical vibration reduces tension and increases proprioceptive sharpness. -
Focused Attention
Sensory immersion and rhythmic cues stabilize the attentional system. -
Physical and Emotional Reset
Zero-gravity posture and deep rhythmic input help users “start fresh,” improving readiness for subsequent tasks.
Shiftwave does not boost performance pharmacologically—it supports the state in which performance naturally thrives.
4. Observational Performance Outcomes From Field Deployments
Across humanitarian, tactical, and high-burnout environments, participants consistently reported:
-
improved clarity
-
reduced overwhelm
-
faster return to baseline
-
increased ability to perform under pressure
LA Wildfire Responders (N = 35)
Reported immediate improvements in mental clarity and readiness after 10–20 minute sessions.
COVID ICU Staff (N = 24)
Participants described using Shiftwave to “reset” between emotionally and cognitively demanding patient loads.
Combat Medics & Evacuation Drivers (N = 48 combined)
Reported feeling “clearer,” “more focused,” and “more level-headed” returning to mission demands.
Ukrainian Rehabilitation Centers (N = 59)
Participants described immediate reductions in tension and improved readiness for therapy sessions.
These qualitative reports align with documented reductions in anxiety and tension—both closely tied to restored performance capacity.
5. Controlled Study: Cognitive-Related State Improvements
In the Lisova Polyana 210-person structured evaluation:
-
22.1% reduction in state anxiety
-
Strong effect sizes (d = 0.89 for anxiety; d = 0.76 for pain)
Since stress and pain are known to impair performance, their reduction supports improved readiness and clarity.
6. Performance Reset: A Rapid Daytime Re-Optimization Protocol
Similar to the Synthetic Sleep concept for restoration, Shiftwave also supports a Performance Reset—a short, high-impact session that shifts the system from fatigue or stress back into a high-engagement state.
Users report:
-
rapid restoration of focus
-
improved reaction time
-
reduced cognitive fog
-
greater emotional steadiness
Preliminary lab observations show:
-
increased prefrontal alpha (associated with calm focus)
-
improved interoceptive clarity (linked to performance consistency)
-
reductions in cognitive stress load (Shiftwave pilot data)
This protocol is not a “performance enhancer” but a state optimizer, supporting rapid readiness transitions between high-demand cycles.
7. Conclusion
High performance requires balanced autonomic function, physical readiness, attentional stability, and emotional clarity. Scientific research strongly supports the role of:
-
breath regulation
-
mechanoreceptor stimulation
-
multisensory immersion
-
postural unloading
in achieving these states.
Shiftwave integrates these evidence-backed modalities into one effortless experience that helps users:
-
reset quickly
-
regain clarity
-
reduce performance-limiting tension
-
access a state of calm focus
Shiftwave makes no medical performance claims. It is a general wellness technology designed to support readiness, clarity, and high-functioning states in everyday and high-demand environments.
References
Autonomic Regulation & Performance
Hansen, A. L., et al. (2003). Vagal influence on working memory and attention. Biological Psychology, 64(1), 177–190.
Laborde, S., et al. (2017). HRV and executive functioning: A meta-analysis. Biological Psychology, 130, 241–255.
Suvada, J., et al. (2020). Sympathetic arousal and decision-making. Neuroscience Letters, 715, 134601.
Breathwork & Performance
Jerath, R., et al. (2006). Physiology of slow breathing and autonomic shift. Medical Hypotheses, 67, 566–571.
Ma, X., et al. (2017). Diaphragmatic breathing and emotional regulation. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 874.
Zaccaro, A., et al. (2018). Breath-control and cognitive/affective modulation. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 353.
Vibration & Physical Readiness
Cardinale, M., & Bosco, C. (2003). WBV and athletic performance. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 17(3), 622–633.
Kerschan-Schindl, K., et al. (2001). WBV and muscle blood flow. Clinical Physiology, 21, 377–382.
Ritzmann, R., et al. (2014). Vibration and proprioception. Eur. J. Applied Physiology, 104, 423–433.
Sensory Immersion & Attention
Annerstedt, M., et al. (2013). Nature soundscapes & physiological recovery. Physiology & Behavior, 118, 240–250.
Brewer, J. A., et al. (2011). Meditation & DMN modulation. PNAS, 108(50), 20254–20259.
Ishimatsu, T., et al. (2021). Acoustic entrainment and attentional stability. Sleep Medicine, 83, 108–116.
Lindquist, K. A., et al. (2012). Neural basis of emotion & attentional control. Behav. Brain Sciences, 35, 121–143.
Shiftwave Internal Sources
Field Deployments — performance-related qualitative outcomes.
Rouse, J., & Serdiuk, K. (2025). Impact of Shiftwave Technology on Pain and Anxiety Scores.
Shiftwave-A Pilot Data — cognitive stress & alpha activity findings.




How Shiftwave Supports Feeling Less Pain and More Physical Ease
How Shiftwave Supports Sleep Quality & Nighttime Relaxation